A handful of police departments that use Flock have unwittingly leaked details of millions of surveillance targets and a large number of active police investigations around the country because they have failed to redact license plates information in public records releases. Flock responded to this revelation by threatening a site that exposed it and by limiting the information the public can get via public records requests.
Completely unredacted Flock audit logs have been released to the public by numerous police departments and in some cases include details on millions Flock license plate searches made by thousands of police departments from around the country. The data has been turned into a searchable tool on a website called HaveIBeenFlocked.com, which says it has data on more than 2.3 million license plates and tens of millions of Flock searches.
The situation highlights one of the problems with taking a commercial surveillance product and turning it into a searchable, connected database of people’s movements and of the police activity of thousands of departments nationwide. It also highlights the risks associated with relying on each and every law enforcement customer to properly and fully redact identifiable information any time someone requests public records; in this case, single mistakes by individual police departments have exposed potentially sensitive information about surveillance targets and police investigations by other departments around the country.
Flock is aware of the exposure enabled by its own product design and has tried to do damage control with its law enforcement customers by blaming “increased public records act/FOIA activity seeking by the public,” according to an email Flock sent to police obtained via public record request. Flock has threatened Cris van Pelt, the creator of HaveIBeenFlocked, by going after his web hosts and claiming that he has violated their intellectual property rights and is posting information that “poses an immediate threat to public safety and exposes law enforcement officers to danger.” In recent weeks Flock severely limited the amount of information available on its audit logs, which are designed to be a transparency tool, raising questions about how much information journalists, regulators, and government agencies will be able to get about police use of Flock cameras in the future.
“I set up HaveIBeenFlocked to show how pervasive and prevalent this monitoring is, and to show just how many searches are getting done. That information, by itself, is shocking,” van Pelt told 404 Media. “To me, as a private citizen, that’s shocking, and I think that’s kind of what Flock is trying to hide or bury.” van Pelt added that he is committed to keeping the website online.
As 404 Media has reported before, Flock’s automated license plate reader cameras are connected to local, state, and/or national “networks” of cameras. When a police officer runs a search seeking the locations of a specific license plate, they are usually not just searching cameras owned by their own jurisdiction, they are usually searching all Flock cameras in that state or in the country. Each individual search creates a record of that search on as many as 80,000 different cameras around the country.
As a compliance and transparency measure, these search records can be obtained through a “search audit,” which are essentially huge spreadsheets of specific Flock searches that contain not just the searches of local police but of all police who have ever searched that camera. Using this data, we have previously been able to report that local police are regularly giving Immigrations and Customs Enforcement side-door access to Flock cameras, and we also reported that Texas searched tens of thousands of cameras nationwide for a woman who self-administered an abortion. Flock search audits have also been used to catch police who have allegedly illegally stalked people or otherwise abused the system.
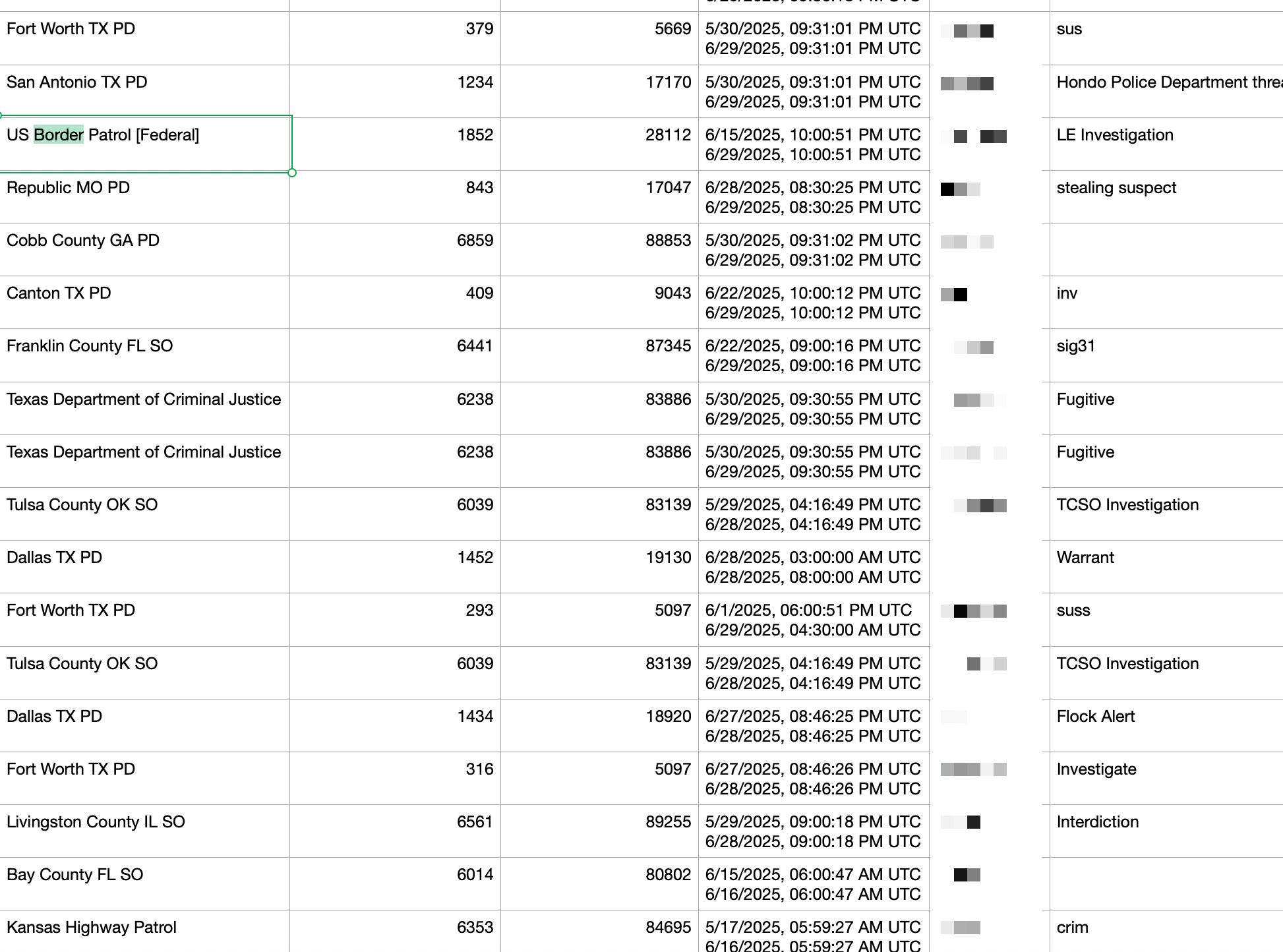
Because these search audits are important tools for police transparency and accountability, they have become a popular type of public record to request for journalists, concerned citizens, privacy experts, city councils, and government regulators. In the vast majority of cases, the police departments releasing the search audit files redact the surveillance target’s license plate number. But in recent months, at least four police departments have released full Flock search audits without redacting anything at all, revealing information about a mix of more than a million individual surveillance targets, suspects, and crime victims. This means that any individual Flock customer could accidentally leak the specific search targets for millions of Flock searches nationwide; any single failure point anywhere in the country could dox the police activity and surveillance targets of other police departments elsewhere.
With the license plate information, you can determine not just what police are using Flock for, but who they are using it against. An unredacted search log file obtained by 404 Media shows more than 700,000 individual searches from June 2025 alone, performed by hundreds of law enforcement agencies nationwide, including hundreds of searches performed by US Border Patrol agents. They show the specific date and time of a search, the name of the officer who did the search, sometimes show the specific case number of a search, the police-stated “reason” of a search, as well as the number of Flock cameras searched. Crucially, they also show the license plate, allowing someone to connect a specific license plate and therefore person to reasons like “drug trafficking,” “fugitive,” “narc,” immigration enforcement, “homicide,” “oil and gas theft,” etc. As the Electronic Frontier Foundation found, they also expose the victims of a host of biased policing tactics and dubious searches, including hundreds of searches of “No Kings” protesters, audit log reasons that included “possible gypsy,” and the search for a woman who had a self-administered abortion.
“EFF has had this [unredacted] information but we’ve chosen not to publish it or share it because of concerns about doxing people—our policy is not to release data of surveillance victims,” Cara Gagliano, a senior staff attorney at the EFF, told me.
404 Media has also had unredacted versions of some of these files for months but has not published any of them. At first, just one or two police departments failed to do redactions. In recent weeks, however, it has become clear that many police departments are not redacting license plates; this led van Pelt to create HaveIBeenFlocked.com, a website that collates many of these search audit logs and allows people to search individual license plates to determine if they have been run through the Flock system, and if so, where and when. The number of police departments who have now released fully unredacted logs has become so numerous that it can no longer be ignored, and the releases have caused Flock to drastically reduce the amount of information that can be obtained from a search audit.
Rather than simply making sure that search audits exported for public records requests do not include license plates or are redacted by default, Flock has totally overhauled how the search logs work; in a December email to police customers obtained by 404 Media, Flock said that “to protect officer safety and active investigations, Network Audit Logs will no longer include: officer names, specific plates searched, vehicle fingerprint information.”
To be clear, Flock is not turning on license plate redaction by default: It is fully withholding officer names and license plate information from the police departments themselves.
“Flock is doing their best to have it both ways where they have no responsibility and also no accountability to the communities where their cameras are placed,” Chris Gilliard, privacy expert and author of the forthcoming Luxury Surveillance, told 404 Media. “Shoddy data hygiene by law enforcement is not seen as a threat or danger but accountability and transparency are.”
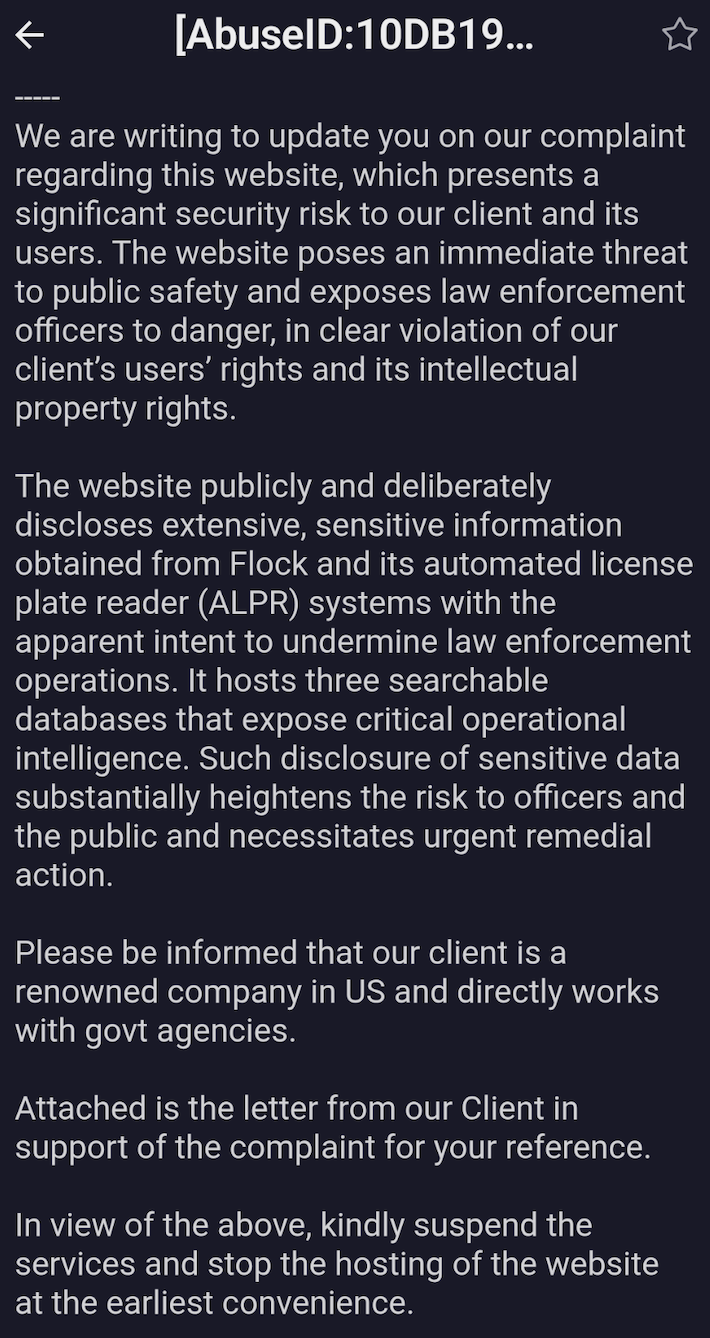
In recent weeks, Flock, via a third party company called Cyble, has threatened van Pelt by filing bogus intellectual property takedown requests with Cloudflare and Hetzner, two of his web hosts. Takedown requests filed by Cyble state the site “presents a significant security risk to our client and its users. The website poses an immediate threat to public safety and exposes law enforcement officers to danger, in clear violation of our client’s users’ rights and its intellectual property rights. The website publicly and deliberately discloses extensive, sensitive information obtained from Flock and its automated license plate reader systems with the apparent intent to undermine law enforcement operations. It hosts three searchable databases that expose critical operational intelligence. Such disclosure of sensitive data substantially heightens the risk to officers and the public and necessitates urgent remedial action.”
“Please be informed that our client is a renowned company in the US and directly works with government agencies,” it continues. “In view of the above, kindly suspend the services and stop the hosting of the website at the earliest convenience.”
The EFF’s Gagliano told 404 Media that, though the EFF hasn’t published license plate information, “these takedowns are bogus. They’re blatantly misrepresenting saying this data is obtained from Flock—no, it’s data obtained from public records. There are issues around deciding whether you should make it all widely available, but it was received from public government agencies and Flock really doesn’t have much standing to be taken down.”
Cloudflare refused to take action on HaveIBeenFlocked, saying that it “found insufficient evidence of a violation,” according to an appeal email van Pelt shared with 404 Media.
Flock told 404 Media in an email “That website that is doxxing cops during active investigations. Today, we’re busy working with journalists to cover the fact that our technology was pivotal in cracking open the case that found the Brown university / MIT serial killer in New England. If you’d like to report the news that matters, we’d be happy to speak to you about bringing justice to victims instead of activists trying to let murderers go free.” Cyble did not respond to a request for comment.
In a December email to police customers titled “What you Need to Know About Recent Online Disclosures,” a Flock executive said “We are aware that agencies across the country, particularly in states with broad public-records laws, are seeing increased PRA/FOIA activity seeking, among other things, LPR search logs. Recently, a third-party website began aggregating search information that has been released through these public-records processes.
We recognize that seeing investigative search activity displayed publicly can raise understandable concerns about officer safety, investigative integrity, community perception, and compliance with state law.”
The email added “To be clear: Flock has not been breached or compromised. We are CJIS compliant. Regardless, we are continuing to make changes to our Product to better protect you and your officers.”
That much is true, because in this case the sensitive material released was taxpayer-funded public records willingly released by police departments around the country.
On the HaveIBeenFlocked website, van Pelt defends his decision to run the site: “This website aggregates and reformats already-public information. This information represents a fraction of what’s being shared with Flock and its government, commercial, and private partners on a daily basis,” he wrote. “Policies exist to prevent the release of this information—they are not adhered to. Laws and regulations exist to enforce the policies—they go unenforced. Police, Flock, and politicians have been ignoring these problems for years while your private movements continue to be collected, catalogued, sold and traded.”
“This website exposes the problem because, as the old saying goes, sunlight is the best disinfectant. Law enforcement and legislation are needed to address the cause of the problem, and we highly encourage you to bring this site to the attention of your legislators,” he added. “We believe mass surveillance has no place in a free society, and this data should not be collected to begin with. If it is collected, warrants should be used, lookups should be rare, and police and private parties, like Flock and HaveIBeenFlocked.com, should not be permitted to act without functional restraints or oversight.”
A police accountability advocate who has seen the unredacted search audits but asked to remain anonymous because Flock has suggested such people are attacking the company and the police told 404 Media that the situation highlights broader problems with Flock.
“It could lead one to the conclusion that if that is an unacceptable outcome for customers, maybe they shouldn’t be participating in a nationwide surveillance system,” they said. “The platform is designed to collect as much data as possible. They want to make that as widely accessible and searchable as possible. They need the network effect so they can continue collecting data for their AI models. So, I struggle with the company’s framing of what’s happened. That framing is an attempt to dodge accountability for what their platform is doing which is collecting data without people’s (and often informed elected officials’) consent.”
Flock going after HaveIBeenFlocked on dubious intellectual property grounds is similar to its strategy against DeFlock, a website that hosts an open source map of ALPR locations.
In a separate December email to Jim Williams, the police chief of Staunton, Virginia, Flock CEO Garrett Langley claimed that public records were being weaponized against the company. Langley claimed the company and police are under “coordinated attack” by activists “trying to turn a public records process into a weapon against you and against us.”
“Flock is building tools to help you fight the real crime affecting communities across the country. Many activists don’t like that. Let’s call this what it is: Flock, and the law enforcement agencies we partner with, are under coordinated attack. The attacks aren’t new. You’ve been dealing with this for forever, and we’ve been dealing with this since our founding, from the same activist groups who want to defund the police, weaken public safety, and normalize lawlessness. Now, they’re producing YouTube videos with misleading headlines,” Langley wrote. “They’re also trying to turn a public records process into a weapon against you and against us. Make no mistake, we’re fighting this fight for you, and, I hope, with you. I remain committed to building world-class technology to help you keep your communities safe. And doing so in a transparent, secure, and privacy centric way.”
Williams responded to Langley:
“As far as your assertion that we are currently under attack, I do not believe that this is so. I have dedicated the last 41 years of my life to serving the citizens of the City of Staunton as a police officer, the last 22 as the police chief,” he wrote. “What we are seeing here is a group of local citizens who are raising concerns that we could be potentially surveilling private citizens, residents and visitors and using the data for nefarious purposes. These citizens have been exercising their rights to receive answers from me, my staff, and city officials, to include our elected leaders. ln short, it is democracy in action.”
In a press release, the Staunton called Langley’s email “unsolicited” and said “The City of Staunton wants to make it clear that the Flock Safety CEO’s narrative does not reflect the city’s values.” Staunton canceled its Flock contract days later.
