The Wikimedia Foundation, the nonprofit organization that hosts Wikipedia, says that it’s seeing a significant decline in human traffic to the online encyclopedia because more people are getting the information that’s on Wikipedia via generative AI chatbots that were trained on its articles and search engines that summarize them without actually clicking through to the site.
The Wikimedia Foundation said that this poses a risk to the long term sustainability of Wikipedia.
“We welcome new ways for people to gain knowledge. However, AI chatbots, search engines, and social platforms that use Wikipedia content must encourage more visitors to Wikipedia, so that the free knowledge that so many people and platforms depend on can continue to flow
Sustainably,” the Foundation’s Senior Director of Product Marshall Miller said in a blog post. “With fewer visits to Wikipedia, fewer volunteers may grow and enrich the content, and fewer individual donors may support this work.”
Ironically, while generative AI and search engines are causing a decline in direct traffic to Wikipedia, its data is more valuable to them than ever. Wikipedia articles are some of the most common training data for AI models, and Google and other platforms have for years mined Wikipedia articles to power its Snippets and Knowledge Panels, which siphon traffic away from Wikipedia itself.
“Almost all large language models train on Wikipedia datasets, and search engines and social media platforms prioritize its information to respond to questions from their users,” Miller said. That means that people are reading the knowledge created by Wikimedia volunteers all over the internet, even if they don’t visit wikipedia.org— this human-created knowledge has become even more important to the spread of reliable information online.”
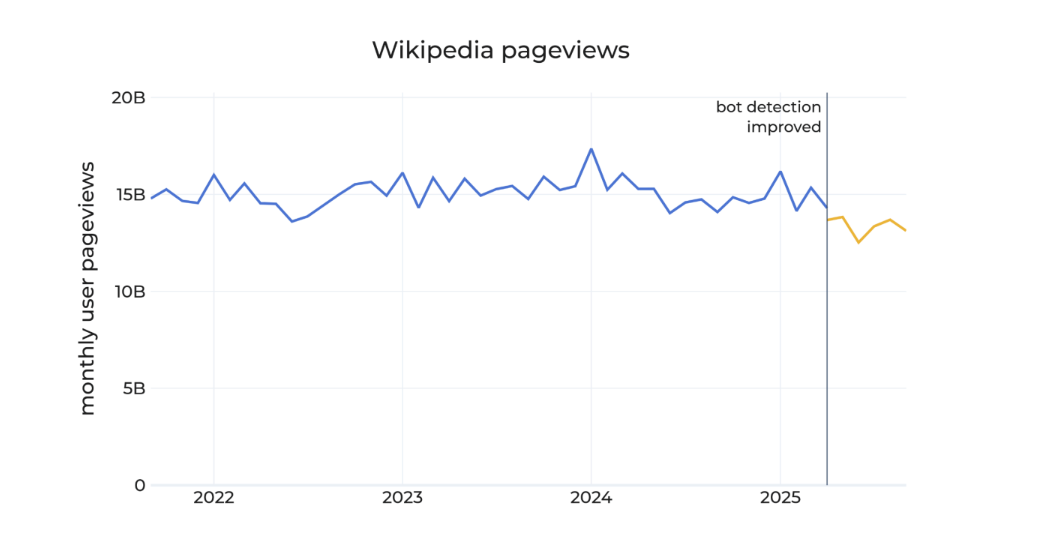
Miller said that in May 2025 Wikipedia noticed unusually high amounts of apparently human traffic originating mostly from Brazil. He didn’t go into details, but explained this caused the Foundation to update its bot detections systems.
“After making this revision, we are seeing declines in human pageviews on Wikipedia over the past few months, amounting to a decrease of roughly 8% as compared to the same months in 2024,” he said. “We believe that these declines reflect the impact of generative AI and social media on how people seek information, especially with search engines providing answers directly to searchers, often based on Wikipedia content.”
Miller told me in an email that Wikipedia has policies for third-party bots that crawl its content, such as specifying identifying information and following its robots.txt, and limits on request rate and concurrent requests.
“For obvious reasons, we can’t share details publicly about how exactly we block and detect bots,” he said. “In the case of the adjustment we made to data over the past few months, we observed a substantial increase over the level of traffic we expected, centering on a particular region, and there wasn’t a clear reason for it. When our engineers and analysts investigated the data, they discovered a new pattern of bot behavior, designed to appear human. We then adjusted our detection systems and re-applied them to the past several months of data. Because our bot detection has evolved over time, we can’t make exact comparisons – but this adjustment is showing the decline in human pageviews.”
The Foundation’s findings align with other research we’ve seen recently. In July, the Pew Research Center found that only 1 percent of Google searches resulted in the users clicking on the link in the AI summary, which takes them to the page Google is summarizing. In April, the Foundation previously reported that it was getting hammered by AI scrapers, a problem that has also plagued libraries, archives, and museums. Wikipedia editors are also acutely aware of the risk generative AI poses to the reliability of Wikipedia articles if its use is not moderated effectively.
“These declines are not unexpected. Search engines are increasingly using generative AI to provide answers directly to searchers rather than linking to sites like ours,” Miller said. “And younger generations are seeking information on social video platforms rather than the open web. This gradual shift is not unique to Wikipedia. Many other publishers and content platforms are reporting similar shifts as users spend more time on search engines, AI chatbots, and social media to find information. They are also experiencing the strain that these companies are putting on their infrastructure.”
Miller said that the Foundation is “enforcing policies, developing a framework for attribution, and developing new technical capabilities” in order to ensure third-parties responsibly access and reuse Wikipedia content, and continues to “strengthen” its partnerships with search engines and other large “re-users.” The Foundation, he said, is also working on bringing Wikipedia content to younger audiences via YouTube, TikTok, Roblox, and Instagram.
However, Miller also called on users to “choose online behaviors that support content integrity and content creation.”
“When you search for information online, look for citations and click through to the original source material,” he said. “Talk with the people you know about the importance of trusted, human curated knowledge, and help them understand that the content underlying generative AI was created by real people who deserve their support.”